# The core of the blockchain is the hash function. Without encryption, the blockchain would be easily manipulated and transactions could be fraudulently inserted.
def update_state(transaction, state): state = state.copy() for key in transaction: if key in state.keys(): state[key] += transaction[key] else: state[key] = transaction[key] return state
# "state" is who owns what record. For example, if I have 10 coins and I give 1 to Medium, then the state would be the value of the dictionary below.
# {"transaction": {"Tom": 9, "Medium": 1}}
# It's important to note that overdrafts cannot exist. If only 10 coins exist, then I cannot give 11 coins to someone. The following function validates that the transaction we are trying to make is indeed valid. Additionally, the transaction must balance. I cannot give 5 coins and have the recipient receive 4 coins because that would destroy and create coins.
def valid_transaction(transaction, state): """A valid transaction must sum to 0.""" if sum(transaction.values()) is not 0: return False for key in transaction.keys(): if key in state.keys(): account_balance = state[key] else: account_balance = 0 if account_balance + transaction[key] < 0: return False return True
# Now, we can generate blocks. We read the information of the previous block and use it to link it to the new block. This is also the core of the blockchain idea. Nominally valid transactions can attempt to fraudulently insert into blockchain but decrypting all previous blocks is (almost) impossible in computation, preserving the integrity of the blockchain.
def make_block(transactions, chain): """Make a block to go into the chain.""" parent_hash = chain[-1]["hash"] block_number = chain[-1]["contents"]["block_number"] + 1 block_contents = { "block_number": block_number, "parent_hash": parent_hash, "transaction_count": block_number + 1, "transaction": transactions } return {"hash": hash_function(block_contents), "contents": block_contents}
# Here's a function to check the hash value of the previous block:
def check_block_hash(block): expected_hash = hash_function(block["contents"]) if block["hash"] is not expected_hash: raise return
# Once we have everything put together, it's time to create our blocks. We now update the blockchain.
def check_block_validity(block, parent, state): parent_number = parent["contents"]["block_number"] parent_hash = parent["hash"] block_number = block["contents"]["block_number"] for transaction in block["contents"]["transaction"]: if valid_transaction(transaction, state): state = update_state(transaction, state) else: raise check_block_hash(block) # Check hash integrity if block_number is not parent_number + 1: raise if block["contents"]["parent_hash"] is not parent_hash: raise return state
# Before we're done, the chain must be validated:
def check_chain(chain): """Check the chain is valid.""" if type(chain) is str: try: chain = json.loads(chain) assert(type(chain) == list) except ValueError: # String passed in was not valid JSON return False elif type(chain) is not list: return False state = {} for transaction in chain[0]["contents"]["transaction"]: state = update_state(transaction, state) check_block_hash(chain[0]) parent = chain[0] for block in chain[1:]: state = check_block_validity(block, parent, state) parent = block return state
# Finally, we need a transaction function that ties everything above together:
def add_transaction_to_chain(transaction, state, chain): if valid_transaction(transaction, state): state = update_state(transaction, state) else: raise Exception("Invalid transaction.") my_block = make_block(state, chain) chain.append(my_block) for block in chain: check_chain(block) return state, chain
# So, now we have 7 functions. How do we interact with it? Well, first we need to start our chain with the Genesis block. This is our beginning of new coins. For the purposes of this article, we'll start with 10 coins.
genesis_block = { "hash": hash_function({ "block_number": 0, "parent_hash": None, "transaction_count": 1, "transaction": [{"Tom": 10}] }), "contents": { "block_number": 0, "parent_hash": None, "transaction_count": 1, "transaction": [{"Tom": 10}] }, } block_chain = [genesis_block] chain_state = {"Tom": 10}
# Now, le


据Odaily报道,去中心化预言机服务PythNetwork宣布其PythEntropy和feed服务已部署至SeiV2。这些服务部署到SeiV2标志着PythNetwork迈出了重要一步,因为它将继续扩展其服务范围并进...


在沃尔玛超市食品区,一袋五常大米的包装袋上增加了二维码,通过微信扫描即可显示信息。首先是基本的产品信息,如规格、制造商、保质期等。;然后是可追溯性信息,包括原材料接收时间、原材料检验报告、产品出厂报告、交货时间、交货时间...


币安同胞们,币安将于2024年2月2日12:00(UTC)上线PythNetwork(PYTH)并开放这些现货交易对的交易。新现货交易对:PYTH/BTC、PYTH/USDT、PYTH/FDUSD和PYTH/TRY。...
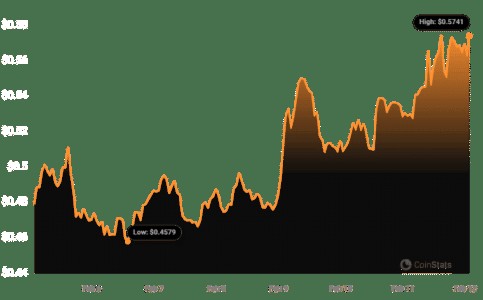

自全球最大的交易所Binance[BNB]在其交易所上市PythNetwork[PYTH]以来已经一周了。上市后PYTH一瞥Bitcoinworld上周报道了币安上市消息传出后PYTH的反应。这一消息加上PYTH的价格上...